Introduction to Rescue SAML 2.0
Document Overview
This document describes how to configure LogMeIn Rescue to use Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0 with your Identity Provider (IDP) (for example, ADFS 2.0).
SAML is an XML framework for transmitting authentication and authorization data over the Internet. Through this framework, SAML enables different security services to exchange and process security information. For making this exchange possible, SAML defines the structure of documents that transport security information between services.
Abbreviations, Definitions, and Acronyms
Abbreviations
- SAML: Security Assertion Markup Language
- IDP: Identity Provider
- MAH: LogMeIn Rescue Master Account Holder
- ADFS: Active Directory Federation Services
- UTC: Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time.
Definitions
- Master Account Holder
- The Master Account Holder is the owner of the LogMeIn Rescue account and has complete control over all areas of the Administration Center. He and the Master Administrators are the only users with access to the Global Settings tab.
- Technicians
- Technicians provide remote support using the LogMeIn Rescue Technician Console. Technicians can choose to run the Technician Console in a supported browser or as a desktop application.
- Administration Center
- Administrators use the LogMeIn Rescue Administration Center to configure LogMeIn Rescue to reflect any support organization; from one support technician, to teams of support technicians with different responsibilities and capabilities. The online interface is used to create and assign permissions for other administrators and Technician Groups. Administrators can also create support channels, which are web-based links that automatically connect customers to technicians.
- Company ID
-
Unique identifier of the Rescue account.
Tip: To obtain your unique company ID, see the sample code under Single Sign-On on the Global Settings tab of the Administration Center.

- Rescue User SSO ID
- A per-technician ID defined in the Single Sign-On ID field on the Organization tab of the Administration Center when adding or editing organization members.
- Certificate Public key/Private key
- Encryption that uses a private/public key pair, thus ensuring that data can be encrypted by one key pair, but only decrypted by the other key pair.
References
- Wiki SAML 2.0: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SAML_2.0
- SAML Specifications: http://saml.xml.org/saml-specifications
- ADFS 2.0: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/adfs2(v=ws.10).aspx
LogMeIn Rescue SAML 2.0 Overview
- SP-initiated
- IDP-initiated
Physical Overview of How Rescue SSO Works
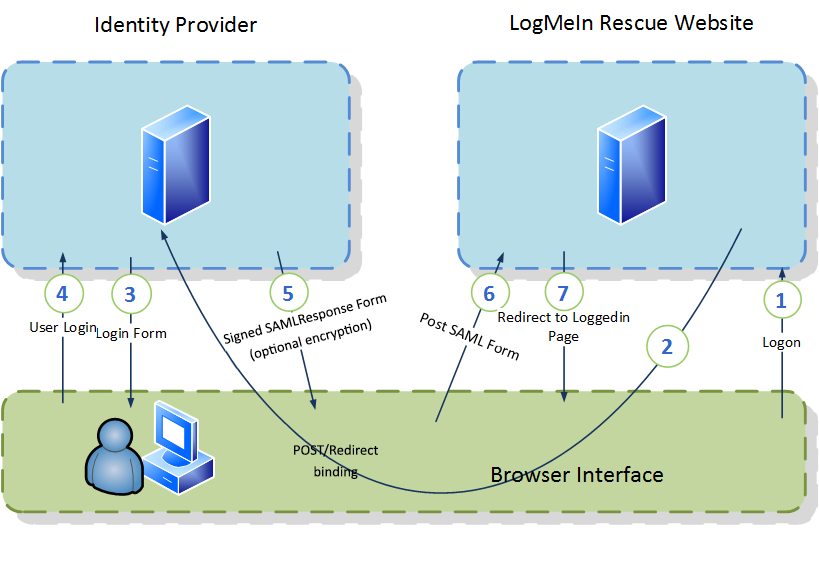
IDP-initiated SSO with POST Bindings
With HTTP POST binding, Rescue responds to a request with a document containing an XHTML form. See Chapter 4.1.1 in the Oasis SAML 2.0 Technical Overview document.
SP-Initiated SSO with Redirect (GET) Bindings
With HTTP Redirect binding, you can send the SAML messages via HTTP GET requests by setting the message as a query string in the URL. See Chapter 4.1.2 in the Oasis SAML 2.0 Technical Overview document.
IDP Requirements
Connection
The Rescue website uses HTTPS communication for HTTP connection. Your IDP must support the HTTP protocol over HTTPS connection (443).
SAML 2.0 Web SSO Profile
Your IDP must support SAML 2.0 Web SSO Profile.
- HTTP POST Binding Authentication Response format
- HTTP Redirect Binding (GET) Authentication Response format
Signature
Rescue validates the signature of the Assertion and Response. You need to sign the Assertion and Response with the same private key.
Response Encryption
The LogMeIn Certificate public key is attached to each assertion request for enhanced security. It is recommended to use the key to encrypt the SAML response that contains assertions in order to protect private data at each end of the SSL pipe.
No further configuration is necessary since Rescue automatically detects if the response is encrypted or not.
Configuration
IDP Configuration
Assertion Consumer Service URL
Important Assertion Configuration for Security Context
- NameID [Required]
-
Name ID is part of the Subject section in the SAML Response message. The IDP must include the user identifier. There are two ways to provide the identifier:
- Technician SSO ID
-
The NameID value contains the Rescue technician SSO ID. It is a property of the Rescue technician and you can edit it in the Admin Center.
Note: The NameID format is not restricted by Rescue.Sample:
<saml:NameID Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent"> jdoe </saml:NameID> - Technician Email
-
The NameID value contains the Rescue technician Email address. It is a property of the Rescue technician and you can edit it in the Admin Center.
Note: The NameID format is not restricted by Rescue.Sample:
<saml:NameID Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:emailAddress"> jdoe@logmein.com </saml:NameID>
- CompanyID Attribute [Required]
-
The IDP must provide the Rescue CompanyID, which is a unique identifier per LogMeIn Rescue account. The certificate is assigned per Rescue account, and we use the CompanyID to find the public key.
Sample:
<saml:Attribute Name="LMIRescue.CompanyID" NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified"> <saml:AttributeValue xsi:type="xs:anyType">123456 </saml:AttributeValue> </saml:Attribute>Tip: To obtain your unique company ID, log in to the LogMeIn Rescue Administration Center, and navigate to . - Language [Optional]
-
If the attribute includes a language code (IETF language tag format), the IDP sends it to Rescue. If the code matches an existing Rescue language, the Rescue website is displayed in that language. See the LogMeIn Rescue Administrators Guide for a list of supported languages.
Sample:
<saml:Attribute Name="LMIRescue.Language" NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified"> <saml:AttributeValue xsi:type="xs:anyType">en-US </saml:AttributeValue> </saml:Attribute>
ADFS 2.0 Configuration
ADFS Relying Party Claim Rules
Edit the Claim Rules
Configure the Claim Rule
ADFS Relying Party Configuration
Configuring LogMeIn Rescue SAML 2.0 with Azure Active Directory
Prerequisites
- An Azure Active Directory Premium subscription (P2 recommended)
- An active LogMeIn Rescue subscription
Configure your Azure Active Directory Account
Configure LogMeIn Rescue
Test the Configuration
Troubleshooting SAML 2.0 Configuration
Basic SAML Error Codes
- RelayStateMissing (1) : The relaystate is not found. The IDP did not provide it.
- RelayStateExpired (2): The relaystate has expired. The login process took too much time.
- ResponseRelayStateIsWrong (3) : The relaystate does not match the expected state. It may be the response for a different request.
- ResponseNotSuccess (4): The response indicates that the authentication failed.
- ResponseDestinationIsWrong (5): The response destination does not match with our address.
- ResponseExpired (6) : The response has expired. The login process took too much time.
- ResponseNotContainAssertion (7) : Fatal error: the response must contain at least one assertion.
- ResponseIssuerIsEmpty (8): The response issuer was empty. The IDP must provide the issuer and it must be the same value as in our configuration.
- AssertionExpired (9) : Assertion has expired. The login process took too much time.
- AssertionSubjectNotValid (10): The assertion contains an invalid subject.
- AssertionSubjectDataAddressIsWrong (11): The assertion subject’s address is wrong. It must match with the target address (the SP address).
- AssertionSubjectNotOnOrAfterNotValid (12): The assertion subject has expired. The login process took too much time.
- AssertionConditionNotOnOrAfterNotValid (13): The assertion condition has expired. The login process took too much time.
- AssertionConditionNotBeforeNotValid (14) : The assertion condition has expired. The login process took too much time.
- IDPConfigurationIsWrong (15) : There is an error with the IDP configuration. Ensure that you configured the Rescue side of the SAML login correctly. Also check the subcode, which may indicate some concrete error.
- ResponseSignatureNotValid (16): The signature of the response is not valid. Ensure that the configured public key is really the public key of the IDP certificate.
- AssertionSignatureNotValid (17) : The signature of the assertion is not valid. Ensure that the configured public key is really the public key of the IDP certificate.
- NameIDNotFound (18): Fatal error: NameID cannot be found in the response. It is key information about the user.
- SAMLComponentError (254): Internal error with the SAML component. This is a Rescue issue.
- UnspecifiedError (255): The cause of the error is unknown.
Rescue Specific SAML Error Codes
- RescueCompanyIDMissing (1) : Company ID is missing. Provide your company ID in the SAML assertion as defined in the documentation.
- ResponseIssuerIsWrong (2): The issuer value of the SAML response is not the same as the configured one. It must be exactly the same value.
- AssertionIssuerIsWrong (3): The issuer value of the SAML assertion is not the same as the configured one. It must be exactly the same value.
- NameIDPolicyFormatMismatch (4): The NameID policy format is different than the configured one. Ensure to provide the same format as in the configuration.
- UnspecifiedError (255) : The cause of the error is unknown.
Rescue Specific Login Error Codes
- loginSAML_UnknownError (999): The cause of the error is unknown. It is probably a Rescue issue.
- loginSAML_InvalidLogin (1120) : Login failed because of an invalid login attempt. It is probably a Rescue issue.
Common Mistakes
- Wrong issuer
-
The Rescue side value of the IDP issuer must be exactly the same as the one posted by the IDP. Even a one-character difference can cause problems.
Remember: Mind casing!
- Wrong company ID
-
The company ID is important because the SAML configuration is stored on a per-company basis. If the IDP sends a wrong company ID, then the correct configuration will not be found, and the login process will fail.
Tip: Take special attention to companies with more than one account (for example, a test and a production account).
- Wrong NameID format
- Rescue provides two ways of being sent the identity of the user: email or SSO ID. These options are mutually exclusive, so the IDP must decide which one to use, and configure the Rescue side with that value. Then the IDP must send the identity in that format.
- Wrong certificate
- Rescue needs the public key of a certain company’s certificate to be uploaded on the Rescue side. If the SAML assertion is signed with a different certificate (for a different certificate there is a different public key) or not signed at all, then we cannot be sure that the request came from a trusted partner, so Rescue cannot let the user log in.
More Rescue Side Troubleshooting
If you are stuck with resolving a problem, check the following:
- Make sure the SAML login is enabled for the company.
- Make sure the user exists in the Rescue system.
Note: "User" here refers to the actual user, not the company.
- Make sure the actual configuration you are stuck with really belongs to the company ID you need.
Tip: Mind test vs production accounts!
- Make sure the certificates are the correct ones.
Appendix: IDP Server Configuration
IIS Configuration
Apache Tomcat Configuration
The default maximum HTTP header size on Apache Tomcat servers is 4096 bytes (4 KB), which should suffice. Check the maxHttpHeaderSize attribute in your server configuration.
For details, see the related Apache documentation.













